PERIMETER ,AREA &VOLUME
- Perimeter of a closed plane figure is the length of its boundary.
- Area of a closed plane figure is the measure of the region (surface) enclosed by its boundary.
- Pythagoras theorem
In a right angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
- Area of a triangle
Area of a triangle = (1/2) × base × height
Also, Area of a triangle = 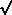 [s (s -a)(s -b)(s-c)] where a, b, c are the lengths of the sides and s = (a +b +c)/2
[s (s -a)(s -b)(s-c)] where a, b, c are the lengths of the sides and s = (a +b +c)/2
Area of an equilateral triangle = 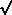 3a²/4, where a is the side.
3a²/4, where a is the side.
- Rectangle
If l = length and b = breadth of a rectangle, then
perimeter = 2 (l +b)
length of diagonal = 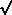 l²+b²
l²+b²
area = l×b.
- Square
If a is the length of side of a square, then
perimeter = 4a
length of diagonal = 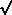 2 a
2 a
area = a²
- Parallelogram
Area of a parallelogram = base×height.
- Trapezium
Area of a trapezium = (1/2) (sum of parallel sides)×height
- Circle
If r is the radius of a circle, then
length of a diameter = 2r
circumference = 2 r
r
area =  r²
r²
Take  = 22/7 (unless given otherwise)
= 22/7 (unless given otherwise)
- Circular ring (track)
If R and r are the radii of two concentric circles then
area of the circular ring (track) =  (R²-r²).
(R²-r²).
- Cuboid
If l, b and h are length, breadth and height of a cuboid, then
Volume = l×b×h
Surface are = 2 (lb +l>h +bh)
Lateral surface area = 2 (l +b)×h
Length of a diagonal = 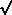 (l² +b² +c²)
(l² +b² +c²)
- Cube
If a be the length of an edge of a cube, then
Volume = a³
Surface area = 6a²
Length of a diagonal = 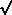 3a
3a
- Let h be the height and a be the side of an equilateral triangle, then h = (
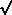 3/2) a.
3/2) a.
- Circumference and area of a circle.
If r is the radius of a circle, then
(i) the circumference of the circle = 2 r
r
(ii) the area of the circle =  r²
r²
- Area of a circular ring.
If R and r are the radii of the bigger and smaller (concentric) circles, then
area of the ring =  (R² -r²).
(R² -r²).
- Circumference and area of a sector of a circle.
If r is the radius of the circle and the arc subtends an angle of n° at the center, then
(i) the length of the arc = (n/360).2 r = n
r = n r/180
r/180
(ii) the area of the sector = (n/360). r²
r²
- Circumference and area of circumscribed and inscribed circles of an equilateral triangle.
If R and r are the radii of the circumscribed and inscribed circles of the triangle, then
(i) R = (2/3)h and r = (1/3)h
(ii) the circumference of the circumscribed circle = 2 R = (4/3)
R = (4/3) h
h
(iii) the area of the circumscribed circle =  R² = (4/9)
R² = (4/9) h²
h²
(iv) the circumference of the inscribed circle = 2  r = (2/3)
r = (2/3) h
h
(v) the area of the inscribed circle =  r² = (1/9)
r² = (1/9)  h²
h²
- Circumference and area of circumscribed and inscribed circles of a regular hexagon.
Let a be the side of a regular hexagon and R, r be the radii of the circumscribed and inscribed circles respectively of the hexagon, then
(i) R = a and r = (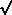 3/2) a
3/2) a
(ii) the circumference of the circumscribed circle = 2 R = 2
R = 2 a
a
(iii) the area of the circumscribed circle =  R² =
R² =  a²
a²
(iv) the circumference of the inscribed circle = 2 r =
r = 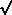 3
3  a
a
(iv) the area of the inscribed circle =  r² = (3/4)
r² = (3/4) a².
a².
- Surface area and volume (of solids)
- Solid Cylinder.
Let r be the radius and h be height of a solid cylinder, then (i) curved (lateral) surface area = 2  rh (ii) total surface area = 2
rh (ii) total surface area = 2  r(h +r) (iii) volume =
r(h +r) (iii) volume =  r²h
r²h
- Hollow cylinder.
Let R and r be the external and internal radii, and h be the height of a hollow cylinder, then
(i) external curved surface area = 2 Rh
Rh
(ii) internal curved surface area = 2 rh
rh
(iii) total surface area = 2 (Rh +rh +R² -r²)
(Rh +rh +R² -r²)
(iv) volume of material =  (R² -r²)h
(R² -r²)h
- Cone.
Let r, h and l be the radius, height and slant height respectively of a cone, then
(i) slant height = 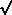 r² +h²
r² +h²
(ii) curved (lateral) surface area =  rl
rl
(iii) total surface area =  r(l +r)
r(l +r)
(iv) volume = (1/3)  r²h
r²h
- Solid sphere.
Let r be the radius of a solid sphere, then
(i) surface area = 4 r²
r²
(ii) volume = (4/3)  r³
r³
- Spherical shell.
Let R and r be the radii of the outer and inner spheres, then
(i) thickness of the shell = R -r
(ii) volume of material = (4/3)  (R³ -r³)
(R³ -r³)
- Solid hemisphere.
Let r be the radius of a hemisphere, then
(i) curved (lateral) surface area = 2 r²
r²
(ii) total surface area = 3 r²
r²
(iii) volume = (2/3)  r³
r³
- Hemispherical shell.
Let R and r be the radii of the outer and inner hemispheres, then
(i) the thickness of the shell = R -r
(ii) external curved surface area = 2  R²
R²
(iii) internal curved surface area = 2 r²
r²
(iv) total surface area =  (3R² +r²)
(3R² +r²)
(v) volume of material = (2/3) (R³ -r³)
(R³ -r³)
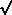 [s (s -a)(s -b)(s-c)] where a, b, c are the lengths of the sides and s = (a +b +c)/2
[s (s -a)(s -b)(s-c)] where a, b, c are the lengths of the sides and s = (a +b +c)/2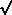 3a²/4, where a is the side.
3a²/4, where a is the side.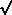 l²+b²
l²+b²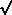 2 a
2 a r
r r²
r² = 22/7 (unless given otherwise)
= 22/7 (unless given otherwise) (R²-r²).
(R²-r²).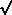 (l² +b² +c²)
(l² +b² +c²)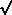 3a
3a  3/2) a.
3/2) a. r
r r²
r² (R² -r²).
(R² -r²). r = n
r = n r/180
r/180 r²
r² R = (4/3)
R = (4/3) h
h R² = (4/9)
R² = (4/9) h²
h² r = (2/3)
r = (2/3) h
h r² = (1/9)
r² = (1/9)  h²
h² 3/2) a
3/2) a R = 2
R = 2 a
a R² =
R² =  a²
a² r =
r =  3
3  a
a r² = (3/4)
r² = (3/4) a².
a². Rh
Rh rh
rh (Rh +rh +R² -r²)
(Rh +rh +R² -r²) (R² -r²)h
(R² -r²)h r² +h²
r² +h² rl
rl r(l +r)
r(l +r) r²h
r²h r²
r² r³
r³ (R³ -r³)
(R³ -r³) r²
r² r²
r² r³
r³ R²
R² r²
r² (3R² +r²)
(3R² +r²) (R³ -r³)
(R³ -r³)